There are some websites you can absolutely get in legal trouble for even visiting, so proceed with the utmost caution. In this guide, we’ll show you what you need to know about how to access the dark web and how to keep yourself safe while you use it. Download Tor Browser to experience real private browsing without tracking, surveillance, or censorship. To make things simpler, HTTP stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol, and this protocol governs communication on the world wide web.
What Is Tor Browser?
The decentralized and often unregulated nature of the dark web means that there is no central authority vetting websites or ensuring their legitimacy. Many links found online may be outdated, leading to defunct services. Others may intentionally be misleading, directing users to scam sites, phishing pages designed to steal information, or even websites hosting malicious software. It is estimated that a substantial percentage of all hidden services are scams, further highlighting the need for extreme caution when navigating this environment. Therefore, users must approach all onion links with a high degree of skepticism and take measures to verify their authenticity whenever possible.
How Do I Keep Myself Safe When On The Dark Web?
But criminals also take advantage of Tor’s anonymity to carry out illegal activities both on and off the dark web. The deep web is the next layer, and it encompasses a massive amount of online data that is not available for public consumption and not indexed by clear web search engines. Deep web content includes academic research papers, court documents, or medical records. For example, when you sign in to your healthcare provider’s portal to view test results or request prescription refills, you’re accessing the deep web. Even in an era of increased online surveillance, the average person on the internet likely has too much to lose to bet on their safety for curiosity’s sake. Heck, I’m one of PCMag’s resident security experts, and I’m not playing around on the dark web just because I know how to.
Using Tor Browser FAQs
You can even organize decentralized communication networks to share benign memes if you want—though it’s probably easier to just use WhatsApp or Discord. You can never be sure of the motive of the person operating the node that your traffic is routed through. Discovered pages are indexed in an extensive database and ranked based on numerous factors. When you search a term (or query) in a web browser, the search engine combs through the database to find relevant results and serves them up on SERPs. However, though the dark web is synonymous with nefarious activity, it does have some benefits.
What Is Tor?
And unlike the Tor browser that only secures the traffic that passes through it, a VPN secures all of your device’s web traffic. Some governments actively monitor dark web activity through various methods, like analyzing internet traffic patterns or using high-end surveillance software. Governments also often set up “honeypot” sites on the dark web, which mimic illegal services and wait for users to enter their info. Of course, this sort of site poses no risk to legitimate dark web users, but it’s worth knowing that your usage of the dark web in general might draw attention to you. The following sections will explain how to access the dark web on different devices.
What Are Onion Sites?

Once you’re secure, download the Tor browser from torproject.org. The Dark Web refers to hidden websites that aren’t indexed by regular search engines like Google or Bing. These websites use special encryption protocols and are accessible only through anonymizing tools like the Tor Browser. When accessing the dark web, using specialized browsers alone isn’t enough. Here’s a practical overview of the most essential tools available in 2025.

Is It Legal To Access The Dark Web?

Instead of the onion routing Tor uses, I2P relies on unidirectional tunnels and garlic routing, which bundles multiple messages together for better traffic obfuscation. It uses its own internal DNS to access “eepsites”, not .onion addresses. Tor protects your identity inside its network, but it doesn’t hide everything. Your ISP still knows you’re using Tor, and entry nodes can see your real IP address.
How Do I Access Tor?
Malicious actors often target browser plugins to steal website credentials or install malware on unsuspecting devices, so Tor sidesteps these risks altogether. Tor uses DuckDuckGo as its default search engine, which is expected for a privacy-focused browser. It doesn’t track your IP address, search history, and other personal data. The entry node knows your IP address but not the intended destination.
Though Tor is slower, the process of rerouting data through nodes makes it more difficult to trace your activity back to you. The “onion routing” technology underpinning the dark web was developed by researchers at the U.S. Initially designed for secure military communications, it evolved into a broader tool for online anonymity, later expanding to public use with the Tor network. To access the dark net and Tor using Brave, open the browser, choose the hamburger icon from the top toolbar, and select Private window with Tor. You will be connected to the Tor network, and then you can open onion websites and obfuscate your network activity.
Then, they can use your data to impersonate you and run social engineering attacks to target your loved ones. You might visit the dark web seeking anonymity or unique services, but this anonymity also attracts scammers. You may encounter fake marketplaces promising illicit goods or services but delivering nothing after payment. The dark web also offers access to blocked resources in countries with strict government censorship on the internet. Citizens of such countries can use the dark web to bypass firewalls and access global information. Be aware, however, that there are sites for absolutely everything, from the benign to the very illegal.
- The last node (exit node), through which Tor routes your traffic, is delicate.
- For information about this, check out our guide on how to get on the dark web.
- Anyone can access the dark web, and it’s not that complicated to do so.
- Regular dark web visitors know that it’s possible to exploit the sketchy reputation of the space and the services offered.
That’s why I’m not going to provide links or detailed instructions for accessing the internet’s shadier side. The dark web — aka, the deep web — is the second layer of the internet, which is not indexed by search engines. Websites and pages in the deep web might include password-protected content, private forums, and personalized resources.
Instead, sites have complex .onion addresses, making them difficult to find without the exact URL. The dark internet is designed to provide anonymity by keeping communication private through encryption and routing online content through multiple web servers. While the dark web is often depicted as an anarchic forum for criminal activity, that’s not necessarily true. The darknet is simply an anonymous space on the web that can be abused or appreciated in turn. One of the most significant dangers is the high likelihood of encountering malware, ransomware, and other forms of malicious software.

Your decisions, responsible conduct, and awareness of potential risks will determine your experience in this hidden realm. In today’s climate, where data breaches and invasive surveillance have become commonplace, understanding how to access the Dark Web and its underlying technologies is becoming increasingly relevant. Whether you’re exploring it out of curiosity or for legitimate personal reasons, it’s essential to approach this hidden realm with the right knowledge, tools, and security measures. Here’s a guide that will help you learn about the dark web, the sites that populate it, and how you can visit it safely using the added protection of a VPN and antivirus software. From journalists and civil society organizations to regular individuals with online privacy concerns, Tor Browser users are a diverse group.
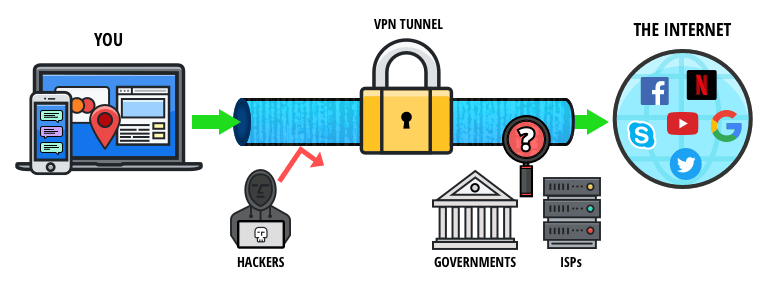
It can only be used to access the content uploaded to the Freenet, which is a peer-to-peer distributed data store. Once you upload something, it stays there indefinitely even if you stop using Freenet, so long as it is popular. A VPN allows a user to encrypt all internet traffic traveling to and from his or her device and route it through a server in a location of that user’s choosing. A VPN, in combination with Tor, further enhances the user’s security and anonymity.